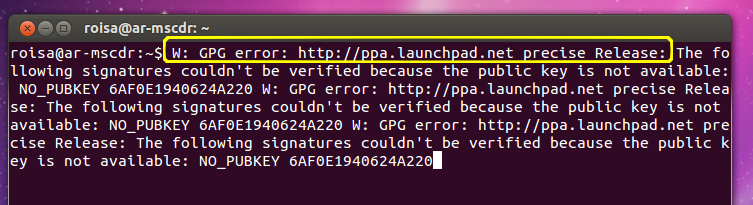
Cas 1 : Si l’erreur apparaît lors d’un sudo apt-get UPDATE :
Le souci vient souvent du dernier paquet installé : history | grep install
- Il suffit de le désinstaller ! REMOVE + PURGE
- Relancer UPDATE
Cas 2 : Si l’erreur apparaît lors d’un sudo apt-get INSTALL :
If the maintainer does not tell you how to add the key then you need to find the “key hash” of the repository in order to look up the key on a public key server. Once you know the key hash, the key can be retrieved using the command:
gpg –keyserver [name of keyserver] –recv-keys [keyhash]
For example, if the key hash is CE49EC21, you retrieve the key using the command:
gpg –keyserver subkeys.pgp.net –recv-keys CE49EC21
Then, add the key to Ubuntu’s apt trusted keys database using the command:
gpg –export –armor CE49EC21 | sudo apt-key add –
Note: There’s a dash at the end of the line above.